When you see piles of waste tires, you might only think of “black pollution”; but in tire recycling factories, a device called a tire wire drawing machine is turning this “rubbish” into high-value rubber and steel wire—like a “bone disassembler” for tires, it precisely separates the metal and rubber in tires, laying the foundation for subsequent renewable resource utilization. Today, we’ll take an in-depth look at this core equipment in the tire recycling industry.
A tire wire drawing machine, also known as a “double-hook wire drawing machine” or “tire steel wire pulling machine” in the industry, is a separation device specifically designed for waste radial tires.
We all know that radial tires (the common tires used on cars and trucks) have dense steel wire rings embedded inside to enhance tire strength—but these steel wires are tightly bonded to the rubber. Manual separation is not only inefficient but also damages the material integrity. The core function of a tire wire drawing machine is to use mechanical force to fully extract the steel wires from the tire, achieving 100% separation of steel wire and rubber, ultimately producing pure rubber strips and intact steel wires that can be further processed into high-purity rubber powder or recycled steel wire.
A tire wire drawing machine is not a “one-size-fits-all machine”; its processing target is tire beads (commonly called “tire rings”) that have had their sidewalls removed, specifically including:
Simply put: it does not handle intact tires, only the “core parts of tires that have been preliminarily disassembled”—after all, intact tires are large and structurally complex, requiring pre-processing by upstream equipment before the wire drawing machine can “take over.”

The operation of a tire wire drawing machine is a highly automated “assembly line process” that requires almost no manual intervention, consisting of 5 specific steps:
1.Loading: “Deliver” the Tire Bead to the Equipment
The operator only needs to place the tire bead on the equipment’s feeding rack—no additional fixing is required, as the equipment will automatically complete subsequent positioning.
2.Clamping + Positioning: “Lock” the Tire Bead in Place
When the equipment starts, it automatically clamps the tire bead and completes precise positioning, ensuring the bead does not shift or wobble during the subsequent pulling process. This step is critical to separation quality: if the bead is misaligned, the steel wire may break, reducing recycling quality.
3.Double-Hook Insertion: Grab the Steel Wire Like “Pliers”
The equipment is equipped with two high-strength alloy steel hooks (compliant with ASTM A514 standards) driven by a hydraulic system, which simultaneously cut into the inner and outer sides of the tire bead—this “double-hook design” is the core: the inner hook grabs the steel wire inside the bead, while the outer hook grabs the steel wire on the outside; bidirectional force ensures the steel wire does not break.
4.Forced Pulling: Fully Extract the Entire Steel Wire
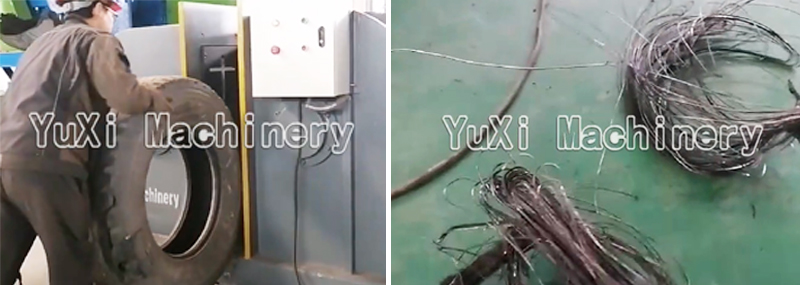
The hydraulic system drives the steel hooks to move outward with strong force (maximum pulling force up to 120kN), and the steel wire is “fully extracted” (rather than broken)—this is the advantage of the tire wire drawing machine: traditional manual or simple equipment tears steel wires into fragments, but the drawing machine produces intact, full-length tire steel wires with higher recycling value.
5.Unloading + Collection: Separate and Recycle Rubber and Steel Wire
After separation, the rubber strips automatically fall into the collection hopper, while the intact steel wires are collected separately—at this point, the tire bead is completely disassembled into two recyclable materials: rubber and steel wire.
Tire wire drawing machines have gained popularity in the tire recycling industry due to these 4 “hard strengths”:
1.High Efficiency and Power: Process Hundreds of Beads Per Day
The double-hook design + hydraulic drive allows it to apply internal and external force simultaneously, enabling fast pulling speeds and high efficiency—according to industry data, a medium-sized tire wire drawing machine (equipped with a 75HP motor) can process 150-250 tire beads per day, far exceeding manual labor (which can handle at most 10 per day).
2.Complete Separation: Higher Purity for Rubber Powder
It achieves “residue-free separation” of steel wire and rubber, and the subsequent rubber powder can reach a purity of over 99.2%—the higher the purity, the higher the market value (e.g., high-purity rubber powder can be used to produce rubber products or modified asphalt compliant with ASTM D6114 standards).
3.Durability: Core Components Are “Tough”
Core components such as steel hooks and clamping devices are made of ASTM A514 high-strength alloy steel + quenched (hardness HRC 45-50), which can withstand high pulling forces and have a service life of 4-6 years—making them a “low-investment, high-return” device for recycling plants.
4.Automated Operation: Reduce Labor and Costs
Except for “loading the tire bead,” the entire process is fully automated—this not only reduces workers’ labor intensity (no need to manually pull steel wires) but also cuts labor costs, making it especially suitable for large-scale recycling plants.
In Europe and the United States, the use of tire wire drawing machines must meet strict environmental requirements:

The implementation of these standards makes the tire wire drawing machine not just an “efficiency tool” but also an “environmental weapon”—it transforms waste tire recycling from a “pollution hazard” into a “compliant resource cycle.”
Today, more and more European and American environmental protection enterprises are investing in tire recycling, and tire wire drawing machines— as “essential equipment”—are constantly upgrading (e.g., smarter positioning systems, faster pulling speeds). Next time you see a waste tire, you might think: in some factory, a wire drawing machine is turning it into a valuable “treasure.”